
Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of streptococcus thermophilus
Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in

Epoxy resin is a staple in electronics, new energy vehicles (NEVs), wind power, and construction due to its superior adhesion, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation. Yet its inherent flammability (LOI = 19.8%) and the environmental risks of traditional halogenated flame retardants have become critical pain points.
As 2025 global regulations tighten—including EU PFAS bans and U.S. CPSC flammability standards—Melamine Polyphosphate (MPP), a halogen-free phosphorus-nitrogen (P-N) synergistic flame retardant, has emerged as the gold standard. Its optimized low-temperature synthesis, excellent compatibility with epoxy resins, and UL94-V0 flame-retardant performance (without compromising mechanical properties) make it indispensable for high-end manufacturing.
This article dives into MPP’s innovative synthesis, synergistic mechanisms, application data, and global compliance strategies, serving as a must-read guide for material engineers and chemical professionals.
MPP is a white powdered halogen-free flame retardant synthesized from melamine and polyphosphoric acid, with properties tailored for high-performance epoxy composites:
Chemical composition: P-N synergistic structure with 21–23% phosphorus content, ensuring efficient flame retardancy.
Physical features: Low water solubility (0.05–0.70 g/L at 20–100℃), fine particle size, and uniform dispersion in epoxy matrices.
Thermal stability: 1% weight loss temperature >380℃, decomposing between 386.5–780℃ to form a dense protective char layer and non-flammable gases.
Traditional MPP synthesis requires high temperatures (>320℃), leading to high energy consumption, yellowing, and poor thermal stability. The patented low-temperature process—validated in industrial applications—solves these issues while cutting costs.
MPP is produced via a three-step reaction with a special additive to enhance polymerization and reduce processing temperature:
Key reaction:
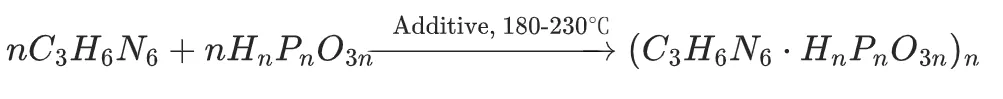
Additive role: Urea, ammonium bicarbonate, or biuret acts as a polymerization promoter and decolorizer, preventing yellowing and boosting thermal stability.
| Performance Indicator | Traditional Process (>320℃) | Optimized Process (180-230℃) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | High | 30–40% lower |
| Product Color | Yellowish | Pure white (suitable for light-colored products) |
| Thermal Stability (1% Weight Loss Temp) | <360℃ | >380℃ |
| Production Cost | High | 15–20% lower |
MPP achieves efficient flame retardancy in epoxy resin through a dual-phase synergistic mechanism, outperforming single-component flame retardants while preserving.
Condensed Phase (Dominant)
Gas Phase (Synergistic)
MPP exhibits exceptional synergistic effects with other flame retardants, reducing addition levels and improving overall performance:
When added at 15–25 wt% (optimal: 20 wt%), MPP-modified epoxy resin delivers:
MPP’s versatility makes it ideal for high-demand, flame-retardant-critical fields:
Electronics: 5G base station insulation parts, circuit board substrates, and electronic packaging materials (high insulation + flame retardancy).
New Energy Vehicles: Power battery potting glue, motor insulation coatings (resistant to high temperature and vibration).
Wind Power: Wind turbine blade adhesives and composites (weather resistance + flame retardancy).
Construction: Flame-retardant coatings, fireproof cables, and structural adhesives (complies with GB 8624-2012 Class A and U.S. 16 CFR 1610 Class 1).
Textiles: Flame-retardant fabrics for furniture and industrial use (meeting EU and U.S. textile flammability regulations).
Halogen-Free & Environmentally Friendly
No toxic gases (e.g., brominated compounds) or corrosive fumes are released during combustion. It is PFAS-free, aligning with 2025 global environmental regulations.
Excellent Compatibility & Thermal Stability
MPP’s high decomposition temperature (>380℃) matches epoxy resin’s processing temperature (150–200℃), avoiding thermal degradation during production. Its fine particle size ensures uniform dispersion, minimizing performance loss.
Cost-Effective Synergistic Performance
P-N synergism and compatibility with other flame retardants (AP, DOPO) reduce MPP addition levels to 20 wt% (vs. 30–40% for single-component alternatives), cutting material costs.
Easy to Integrate
As an additive flame retardant, MPP requires no modifications to existing epoxy resin processing equipment. It is compatible with solvent-free, BPA-free epoxy systems for eco-friendly manufacturing.
Melamine Polyphosphate (MPP) addresses the industry’s dual challenges of epoxy resin flammability and regulatory compliance through its innovative low-temperature synthesis, P-N synergistic mechanism, and compatibility with high-end manufacturing needs. As 2025 global regulations (EU PFAS bans, U.S. CPSC standards) take effect, MPP’s halogen-free, low-smoke, and cost-effective properties position it as the preferred flame retardant for electronics, NEVs, and construction.
With ongoing advancements in synergistic systems (e.g., MPP + nano-fillers) and broader adoption in eco-friendly epoxy formulations, MPP is poised to dominate the halogen-free flame-retardant market, driving sustainable growth in the chemical materials sector.

Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in

Tech Blog Melamine Modified Polyurethane Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer celebrated for its excellent wear resistance, oil resistance, chemical stability, and strong adhesion to

Tech Blog Spectrophotometric Method for Melamine Detection The spectrophotometric method for melamine detection is based on the complexation reaction between melamine powder, formaldehyde, and carbonyl

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE