
Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of streptococcus thermophilus
Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in

Melamine molding compound powder is a key material for manufacturing durable and heat-resistant products, such as tableware, electrical components, and automotive parts. Strict quality testing is crucial to ensure compliance with safety standards and that the product meets the requirements of different application scenarios. This article introduces the aspects and testing methods that need to be used to detect melamine molding powder.

Purpose:
To ensure uniform particle size for consistent flow and shaping.
Method:
Screening method: A certain amount of melamine molding compound powder is passed through a series of standard sieves with different pore sizes, and the proportion of powder in different particle size ranges is calculated based on the mass of powder remaining on each sieve. This method is simple to operate but has limited screening accuracy for finer powders.
Laser particle size analysis method: Using the principle of laser scattering, the scattered light intensity distribution of powder particles in the laser beam is measured to obtain the particle size and distribution of the particles. This method has the advantages of fast measurement speed, high accuracy, and good repeatability. It can detect powders with a wider range of particle sizes.
Purpose:
To affect compression molding efficiency and final product density.
Method:
True density measurement: Using the density bottle method, first wash, dry, and weigh the density bottle. Then, add a certain amount of powder, weigh again, and add a known-density liquid (such as anhydrous ethanol) to the bottle to completely immerse the powder, remove bubbles, and weigh. The true density of the powder can be determined through calculation.
Loose density measurement: The powder is freely dropped into a container of known volume in a certain way, and the mass of the powder in the container is weighed to calculate the loose density of the powder. The loose packing density reflects the compactness of the powder in its natural stacking state. It has a significant impact on the subsequent molding process.
Purpose:
To evaluate the ability of powder to uniformly fill molds.
Method:
Hall flowmeter: Pass the powder through a standard funnel and measure the time required for all the powder to flow out of the funnel to evaluate the powder’s flowability. The faster the flow rate, the better the flowability of the powder.
Measurement of angle of repose: Powder is freely dropped from a certain height and stacked into a cone, and the angle between the generatrix of the cone and the horizontal plane is measured, which is the angle of repose. The smaller the angle of repose, the better the flowability of the powder.
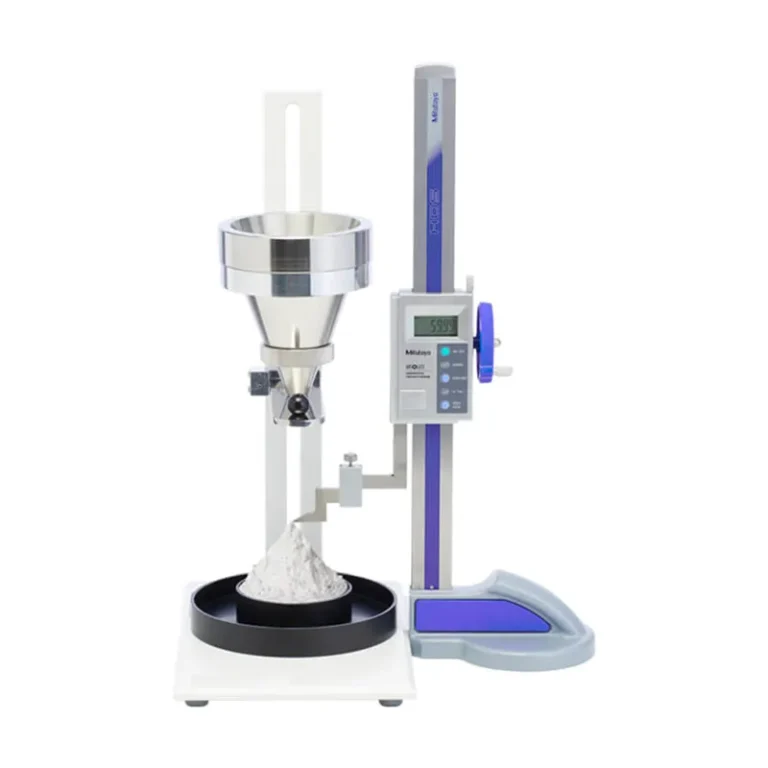

Method:
Elemental analysis: Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and other analytical methods are used to detect the content of various elements in melamine molding powder, ensuring that it meets quality standards. For example, the detection of whether the heavy metal content (such as lead, cadmium, etc.) exceeds the standard to meet food safety or environmental protection requirements.
Functional group analysis: Using techniques such as infrared spectroscopy (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), analyze the types and structures of functional groups contained in the powder to determine whether its chemical composition and molecular structure meet expectations.
Method:
Spectrophotometric method: After processing the powder sample, the formaldehyde reacts with specific reagents to produce colored compounds. The solution’s absorbance is measured by a spectrophotometer, and the formaldehyde content is calculated based on the standard curve. This method is relatively simple to operate and cost-effective and is one of the commonly used formaldehyde detection methods.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): This method separates formaldehyde from the sample and accurately determines its content by detecting its absorption peak area at a specific wavelength. HPLC has the advantages of high sensitivity and good accuracy and is suitable for the detection of products with strict formaldehyde content requirements.
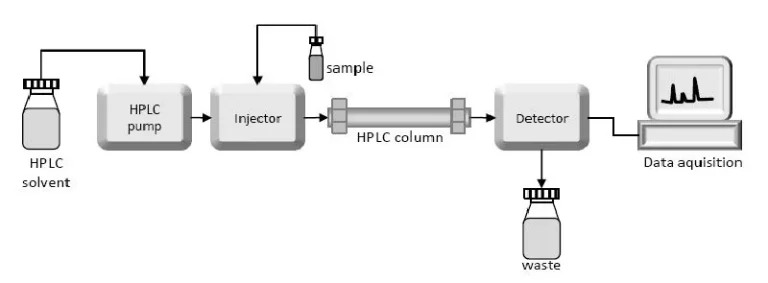
Method:
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA): Measures the relationship between a sample’s mass and temperature changes under program-controlled temperature. The TGA curve can be used to understand the powder’s mass loss during heating and evaluate its thermal stability. For example, it can be used to observe parameters such as the starting temperature and maximum decomposition rate temperature of powders at different temperatures.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC): Measures the relationship between the power difference and temperature of the input substance and reference substance. The DSC curve can reflect the thermal effects of powders during heating or cooling processes, such as glass transition temperature, melting temperature, curing reaction heat, etc., which helps to evaluate the thermal properties and curing characteristics of powders.
Make standard tensile specimens from powder, apply a tensile load to the specimens using a tensile testing machine until they break, and measure their mechanical performance indicators, such as tensile strength and elongation at break. Tensile performance reflects the material’s ability to resist damage under tensile action.
The three-point bending or four-point bending test method applies a bending load to a powder sample and measures its bending strength and modulus. Bending performance is of great significance for evaluating the performance of materials under bending forces.
Apply an impact load to the specimen using an impact testing machine and measure its impact strength. Impact performance reflects the toughness and resistance to damage of materials under impact loads. Common impact test methods include the cantilever beam impact test and the simply supported beam impact test.
Make standard-sized samples of powder under certain molding process conditions, measure the changes in sample size before and after molding, and calculate the molding shrinkage rate. The molding shrinkage rate is an important indicator for measuring the dimensional stability of powder after molding, which is crucial for ensuring the dimensional accuracy of products.
Heat the powder to a certain temperature and record the time it takes to change from a liquid state to a gelled state. The gel time reflects the powder’s curing speed in the molding process, which is an important reference value for determining the molding process parameters (such as molding temperature, molding time, etc.).
The mold has poor flow and a high moisture content (>1.5%). Pre-dry the powder at 80 ° C for 2 hours.
The incomplete curing of bubbles in the product will prolong the curing time by 20-30 seconds.
Optimize the mixing time (20-30 minutes) for uneven dispersion of color stripe pigments.
Comprehensive quality testing of melamine molding compound ensures compliance with global standards (FDA, EU,…). By combining traditional methods such as HPLC and TGA with advanced technologies such as AI-driven detection, manufacturers can achieve consistent quality, reduce waste, and meet constantly changing market demands.

Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in

Tech Blog Melamine Modified Polyurethane Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer celebrated for its excellent wear resistance, oil resistance, chemical stability, and strong adhesion to

Tech Blog Spectrophotometric Method for Melamine Detection The spectrophotometric method for melamine detection is based on the complexation reaction between melamine powder, formaldehyde, and carbonyl

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE