
Arc Resistance of Melamine Molding Compounds
Tech Blog Arc Resistance of Melamine Molding Compounds Melamine molding compounds are essential insulating materials for the electrical and instrumentation industries, widely used in mine


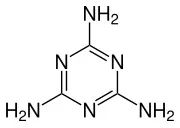
Melamine, named “1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine” by IUPAC, is a triazine nitrogen-containing heterocyclic organic compound and a chemical raw material. It is a white monoclinic crystal, almost odorless, slightly soluble in water, soluble in formaldehyde, acetic acid, hot ethylene glycol, glycerol, pyridine, etc., insoluble in acetone, ether, and harmful to the body. It cannot be used for food processing or food additives.
Melamine chemical formula: C3H6N6
Melamine Cas No: 108-78-1
Melamine molecular weight: 126.12
Melamine melting point: 354 ℃
Melamine boiling point: 557.54 ℃
Melamine Density: 1.661 g/cm³
Melamine Flash Point: 325.3 ℃
Melamine UN No.: 3263
The appearance of melamine powder is white monoclinic crystals. Insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethylene glycol, glycerol, ethanol, insoluble in ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride.
Melamine powder is nonflammable and has stable properties at room temperature. The aqueous solution is slightly alkaline with a pH of 8 and can react with hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid, etc., to form melamine salts. In neutral or slightly alkaline conditions, it condenses with formaldehyde to form various hydroxymethyl melamine.
In somewhat acidic conditions (pH=5.5-6.5), it undergoes a condensation reaction with hydroxymethyl derivatives to form resins. When hydrolyzed by strong acid or strong alkali aqueous solution, the amino group is gradually replaced by the hydroxyl group, first forming cyanuric acid diamide, further hydrolyzed to form cyanuric acid monoamide, and finally formed cyanuric acid.
The primary raw materials for melamine are dicyandiamide or urea.
However, modern commercial production of melamine typically uses urea due to its low cost. Urea is carried by ammonia gas and catalyzed by silica gel. It undergoes a boiling reaction at a temperature of 380-400 ℃, decomposing to form cyanic acid and further condensing to form melamine.
The generated melamine gas is cooled and captured to obtain a crude product, which is then dissolved to remove impurities and recrystallized to get the finished product. The urea method for producing melamine consumes approximately 3800kg of urea and 500kg of liquid ammonia per ton of product.
For more detailed production methods, please read How To Make Melamine Powder?
Melamine powder is the primary raw material used to manufacture melamine formaldehyde resin (MF). Melamine resin can be produced by condensation polymerization with formaldehyde, which can be used in the plastic and coating industries, as well as as an anti-folding and anti-shrinking treatment agent for textiles. Its modified resin can be a metal coating with bright color, durability, and good hardness.
It can also be used for sturdy, heat-resistant decorative sheets, moisture-proof paper, gray leather tanning agents, adhesives for synthetic fireproof laminates, fixing or hardeners for waterproofing agents, etc.
Melamine is the most commonly used gas source for expanding flame retardants and a raw material for preparing many components of expanding flame retardants.
For more detailed information, please read melamine powder uses.
Long-term ingestion of melamine may cause damage to human reproductive capacity, bladder or kidney stones, bladder cancer, etc. For breast-feeding infants who drink less water and have narrow kidneys, stones are more likely to form, and severe cases may even lead to renal failure or death.
There is a clear dose-response relationship between melamine dosage and clinical diseases. The American Journal of Life Science reported that pure melamine has mild toxicity, but melamine is often mixed with cyanuric acid during production.
After melamine enters the human body, it will partially hydrolyze into cyanuric acid in the strongly acidic environment of the stomach. Melamine and cyanuric acid can form an extensive network structure (hydrogen bond structure). After ingestion by the human body, melamine and cyanuric acid are separated by the action of stomach acid, absorbed through the small intestine into the bloodstream, and ultimately enter the kidneys. In renal cells, the two combine and deposit again to form stones, blocking renal tubules and ultimately leading to renal failure.
For more significant adults, stones are less likely to form due to their metabolic solid capacity and frequent drinking of water. However, infants and young children have limited water intake and small kidney volumes, making them susceptible to stone damage. Melamine harms human health and is strictly prohibited from being used in food and animal feed. Melamine may contaminate food at various stages during food processing, transportation, storage, and sales.
Melamine is not banned in all industries and is still widely used in various industrial productions. It is mainly banned in the food-related industry.
There have been cases of melamine being added to edible milk powder before.
In 2008, many infants who consumed milk powder produced by Sanlu Group were found to have kidney stones; subsequently, melamine, a chemical raw material, was found in their milk powder.
According to the released figures, as of September 21, 2008, a total of 39965 infants and young children who received outpatient treatment and consultation due to the use of infant formula have recovered, 12892 are currently hospitalized, 1579 have been cured and discharged, four have died, and as of September 25, 5 people in Hong Kong and one person in Macau have been diagnosed with the disease.
The incident has attracted a lot of attention from various countries and concerns about the safety of dairy products.
For a long time, the “Kjeldahl method” has been used to determine the protein content in food, which indirectly calculates the protein content in food by multiplying the nitrogen content of the food by 6.25. According to the molecular formula of melamine, its nitrogen content can be around 66%. If 0.1g of melamine is added to every 100g of milk, theoretically, the protein content of milk can be increased by 0.625%.
Therefore, melamine is also known as “protein essence” and is illegally added to milk and other foods to improve the “protein” content. Moreover, melamine is white and odorless, making it difficult to detect when mixed into food. Driven by profit, unscrupulous vendors add it to food to improve the apparent protein content index in food testing.
Melamine powder is not a food ingredient, nor is it a food additive. It is prohibited to add it to food artificially. Those who artificially add melamine to food shall be held legally responsible by the law. As a chemical raw material, melamine can be used to produce plastics, coatings, adhesives, and food packaging materials.
Skin contact: Remove contaminated clothing and rinse with plenty of running water.
Eye contact: Lift the eyelids and rinse with water or saline solution. Seek medical attention.
Inhalation: Remove from the scene to a place with fresh air. Seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Drink plenty of warm water and induce vomiting. Seek medical attention.
Hazardous characteristics: Heat decomposition releases highly toxic cyanide gas.
Harmful combustion products: Include carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrogen cyanide.
Fire extinguishing method: Firefighters must wear filter-type gas masks (full face shields) or isolated respirators, full-body fire and gas protective clothing, and extinguish the fire in the upwind direction. It is important to move the container from the fire scene to an open area as much as possible.
Isolate the contaminated area and restrict access.
It is recommended that emergency responders wear dust masks (full face shields) and gas-protective clothing. Collect dry, clean, and covered containers with a clean shovel and transfer them to a safe location.
In the case of a large amount of leakage, it should be collected and recycled, or transported to a waste disposal site for proper disposal.
Precautions for operation:
Closed operation, comprehensive exhaust.
Operators must undergo specialized training and strictly adhere to operating procedures.
It is recommended that operators wear self-priming filter dust masks, chemical safety goggles, anti-toxic work clothes, and rubber gloves.
Avoid generating dust. Avoid contact with oxidants and acids. Handle with care during transportation to prevent damage to packaging and containers.
Equip with emergency response equipment for leaks. Empty containers may contain residual harmful substances.
Storage precautions: Store in a calm and ventilated warehouse.
Stay away from sources of fire and heat. It should be stored separately from oxidants and acids and should be avoided from mixing during storage.
The storage area should be equipped with suitable materials to contain leaked materials.

Tech Blog Arc Resistance of Melamine Molding Compounds Melamine molding compounds are essential insulating materials for the electrical and instrumentation industries, widely used in mine

Tech Blog Influential Factors on Melamine Moulding Compounds Melamine moulding compounds are widely used in electronics, household utensils, and automotive parts due to their excellent

Tech Blog How to Slow Down Melamine Reactor Temperature Difference Rise Rate Melamine production via high-pressure processes (3rd-5th generation) relies heavily on reactor long-cycle operation.

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE