
Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of streptococcus thermophilus
Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in


Melamine IUPAC name is “1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine”, and its chemical formula is C3H6N6.
This indicates that it is composed of three carbon (C) atoms, six hydrogen (H) atoms, and six nitrogen (N) atoms.
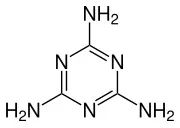
The carbon atoms in melamine form the backbone of its molecular structure.The carbon atoms are bonded in a specific arrangement in melamine powder that gives the molecule its unique shape and properties .
This structure is part of what allows melamine to have a relatively high melting point and good chemical stability.
The hydrogen atoms are attached to the carbon and nitrogen atoms. They play a role in determining the polarity of the melamine molecule.
Although the contribution of hydrogen atoms to the overall properties of melamine may seem less significant compared to carbon and nitrogen, they are essential for maintaining the molecular structure integrity.
The high proportion of nitrogen atoms is a distinctive feature of melamine. The nitrogen atoms are responsible for many of melamine’s key properties.
For example, the nitrogen – rich nature of melamine makes it useful in applications where a high nitrogen content is beneficial, such as in some fertilizers (in the form of its derivatives) and in certain types of resins.
The combination of carbon – carbon, carbon – nitrogen, and nitrogen – hydrogen bonds contributes to the high stability of melamine. These bonds are relatively strong, allowing melamine to withstand high temperatures and resist chemical degradation under certain conditions.
This stability is what makes melamine suitable for use in high – heat environments, such as in some kitchenware applications.
The arrangement of the atoms and the nature of the bonds also affect melamine’s solubility.
Melamine is slightly soluble in water at room temperature (about 3.1g/L) but has different solubility profiles in other solvents depending on the nature of the solvent and the interaction between melamine’s atoms and the solvent molecules.
For example, it is soluble in formaldehyde, acetic acid, hot ethylene glycol, glycerin, and pyridine, while it is insoluble in acetone, ethers, and carbon tetrachloride.
The components of melamine, namely carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms, are characterized by a hexagonal ring arrangement in its molecular structure, which contributes to its stability.
Understanding the relationship between its chemical composition and properties can help better utilize melamine in various industries, while also recognizing its potential limitations and safety issues.

Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in

Tech Blog Melamine Modified Polyurethane Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer celebrated for its excellent wear resistance, oil resistance, chemical stability, and strong adhesion to

Tech Blog Spectrophotometric Method for Melamine Detection The spectrophotometric method for melamine detection is based on the complexation reaction between melamine powder, formaldehyde, and carbonyl

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE