
Fluorescence Detection Of Melamine
Tech Blog Fluorescence Detection of Melamine Melamine powder adulteration in dairy products poses severe health risks, including kidney stones and urinary system disorders. Traditional detection


Urea is a compound of significant importance in various fields, such as agriculture, medicine, and industrial chemistry. Its unique solubility characteristics make understanding its solubility crucial for its application.
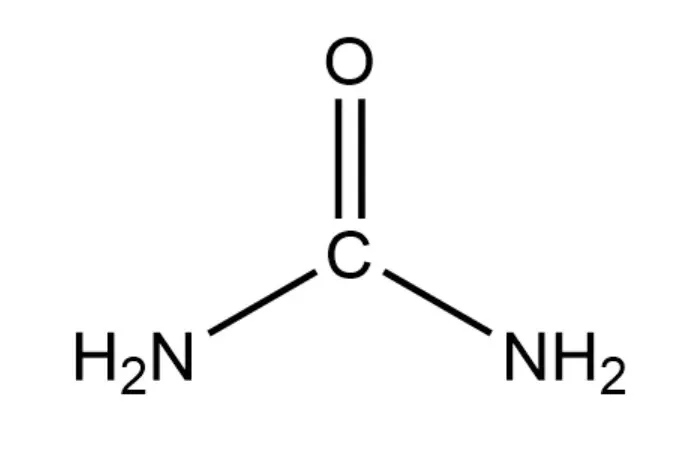
The chemical formula of urea is CN₂H₄O, and the structural formula is H₂N-CO-NH₂. The presence of polar functional groups, especially carbonyl (C=O) and amino (- NH₂) groups, plays a crucial role in determining their solubility behaviour.
Due to the formation of intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonds, polar substances often dissolve well in polar solvents.
Reflected in urea, the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group and the nitrogen atom in the amino group can form hydrogen bonds with solvent molecules, a key factor in its solubility in appropriate solvents.
Water may be the most common and important solvent when considering solubility.
Urea is highly solubilized in water. At room temperature (approximately 25 ° C), about 108 grams of urea can be dissolved in 100 millilitres of water to form a clear and uniform solution.
As the temperature increases, the solubility of urea in water further increases. For example, at 80 ° C, the solubility can reach about 730 grams per 100 millilitres of water.
Understanding this temperature change is of great importance for practical applications, such as in the formulation of urea-based fertilizers, where solubility can affect plants’ nutrient release and availability.
Although urea has a high solubility in water, its solubility in organic solvents varies greatly.
Urea exhibits moderate solubility in polar organic solvents such as methanol (CH3OH) and ethanol (C₂H₂OH). These solvents can form hydrogen bonds with urea. However, due to molecular polarity and structure differences, the hydrogen bonds are not as strong as those in water.
For example, in methanol, urea can dissolve to a degree that allows certain chemical reactions and formulations to occur, which has been utilized in some laboratory and industrial processes that require media with lower polarity but still compatible with urea.
However, in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene (CSH₆) or hexane (CH₂), the solubility of urea is extremely low. These non-polar solvents lack polar functional groups, which hinder the formation of significant hydrogen bonds or other strong intermolecular forces with urea, making it difficult for urea to dissolve and disperse uniformly.
In addition to the temperature mentioned earlier, there are two other aspects:
The pH value of urea also has a certain impact on its solubility.
Urea’s solubility is higher under neutral or slightly acidic conditions, while it decreases under alkaline conditions.
This is because, under acidic conditions, urea forms an NH₂-structure with increased hydrophilicity and is easily soluble in water, while under alkaline conditions, urea forms an NH3+ structure with reduced hydrophilicity and is difficult to dissolve in water.
Ionic strength can also affect the solubility of urea.
The more positive and negative an ion contains the greater the ion strength.
When the ionic strength increases, the solubility of urea also decreases. This is because ions affect the structure of water molecules, making it more difficult for them to dissolve other substances.
In agriculture, the solubility of urea in water is crucial for its use as a fertilizer. Farmers dissolve urea particles in water for foliar spraying or soil irrigation systems, providing plants with a readily available nitrogen source. The ability of urea to quickly dissolve and release nitrogen in a form that plants can absorb is crucial for promoting healthy growth and high yield.
In the industrial field, the solubility of urea in different solvents is used to produce urea resin. For example, in the manufacture of urea-formaldehyde resins for adhesives and plastics, the solubility of urea in methanol or water (depending on the process stage) allows for effective mixing and reaction with formaldehyde to form desired polymer products with specific properties such as strength and durability.
Urea’s solubility is a complex and fascinating aspect of its chemical properties. Its high solubility in water, variable solubility in organic solvents, and sensitivity to temperature and pH all contribute to its wide range of applications.
Understanding and utilizing the solubility of urea is essential for maximizing its potential in different fields, whether it is nourishing crops in the field or transforming it into useful industrial materials.
Continuous research in this field can open up more effective methods for utilizing this versatile compound.

Tech Blog Fluorescence Detection of Melamine Melamine powder adulteration in dairy products poses severe health risks, including kidney stones and urinary system disorders. Traditional detection

Tech Blog Colorimetric Detection Of Melamine Melamine powder, an industrial chemical with high nitrogen content, is illegally added to dairy products to falsify protein levels,

Tech Blog Turbidimeter method for detecting the turbidity of melamine Turbidity is a critical intrinsic quality index for melamine powder, directly reflecting the purity and

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE