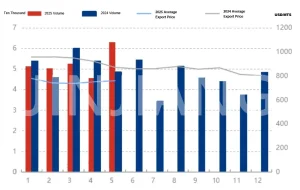
China Melamine Analysis In May.2025
News China Melamine Analysis In May.2025 1. China Melamine Powder Export date In May 2025, melamine powder exports reached 63,000 tons, up 38.16% from the


The production of urea mainly uses ammonia(NH₃) and carbon dioxide(CO₂) as raw materials.
Ammonia and carbon dioxide react under high temperature and pressure conditions to produce ammonium formate, the foundation of urea production. The required ammonia and carbon dioxide must be high purity to ensure the smooth progress of the reaction.
Reaction conditions: Ammonia and carbon dioxide react under high temperatures and pressure. The typical reaction temperature is between 180 ° C and 200 ° C, and the pressure is about 13-24 MPa. Under these conditions, ammonia and carbon dioxide undergo a chemical reaction to produce Ammonium Carbamate(NH₂COONH₄).
Reaction process: Ammonium carbamate is further dehydrated to produce urea(CO(NH₂)₂). This continuous reaction requires precise control of reaction conditions to ensure the yield and quality of urea.
The chemical reaction formula for prilled urea production is shown in Figure 1
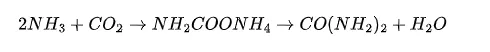
The formation of molten urea: The generated urea is processed through a series of processes to form a molten state. At this time, the urea’s temperature is high, and it has good fluidity.
Spray into granulation tower: Molten urea is sprayed into the granulation tower through a nozzle. The nozzle is designed in a unique shape to spray urea in a mist, forming tiny droplets. These droplets come into contact with air during their descent and rapidly cool and solidify.
Particle formation: Good air circulation in the granulation tower helps to cool and solidify urea droplets. As the droplets fall, they gradually form solid particles. The granulation tower’s height and air circulation velocity significantly impact particles’ formation and quality.

Cooling: After the prilled urea is collected at the bottom of the granulation tower, it is transported to the cooling device through a conveyor belt. The cooling apparatus cools the granular urea to reach the appropriate storage temperature.
Packaging: The cooled prilled urea is packaged in plastic or paper bags for easy storage and transportation. During the packaging process, it is essential to ensure that the packaging is intact to prevent moisture and particle contamination.

Mpurity detection: During production, impurity detection should be performed on prilled urea. Impurities may include unreacted ammonia, carbon dioxide, moisture, etc. Detecting the content of impurities can ensure that the product quality meets the standards.
Particle size and shape: The size and shape of urea particles are also important aspects of quality control. The particle size should be uniform and consistent, and the shape should be regular. This helps to improve the fluidity and storage stability of the product.
Increase yield: Optimize production processes to increase the yield of urea, such as improving reaction conditions or enhancing equipment efficiency.
Cost reduction: Costs must be reduced in the production process. This can be achieved by optimizing raw material procurement and improving energy efficiency.
In short, the production process of urea involves multiple links.
It requires strict control of reaction conditions and quality standards. Continuously optimizing production processes to meet market demand can improve product quality and production efficiency.

News China Melamine Analysis In May.2025 1. China Melamine Powder Export date In May 2025, melamine powder exports reached 63,000 tons, up 38.16% from the

Tech Blog How Melamine Molding Compound Powder Is Revolutionizing Industrial and Household Products Melamine molding compound powder (MMC powder)-thermosetting polymers synthesized from melamine formaldehyde (MF)
Tech Blog Melamine Molar Mass Melamine powder (C₃H₆N₆) is a nitrogen-rich organic compound widely used in industrial and consumer goods, from durable tableware to flame-retardant

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE