
Urea Industrial Use
Tech Blog Urea Industrial Use When most people hear the word “urea,” they immediately think of fertilizer. While it’s true that over 90% of the

Urea, a simple yet vital organic compound, is crucial in various chemical and biological processes. Understanding its chemical structure is fundamental to grasping its properties and functions.
From its use in fertilizers to its role in the human body’s nitrogen metabolism and its importance in industrial applications such as the production of plastics and resins, the chemical structure of Urea is the key to unlocking its diverse potential.
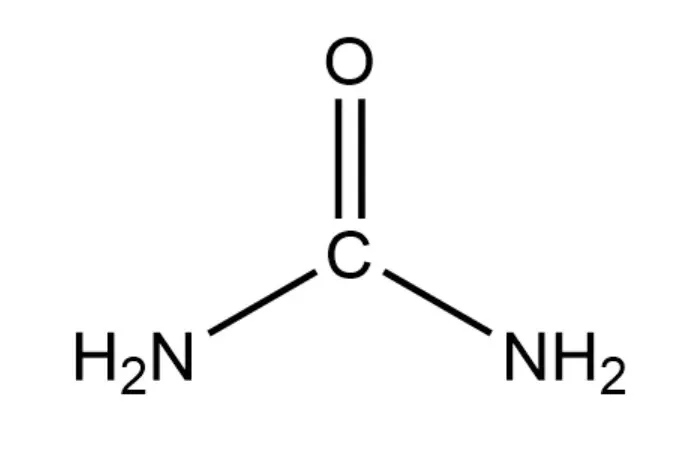
Urea structural formula CH₄N₂O. It consists of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O) atoms. At a molecular level, it contains one carbon atom, four hydrogen atoms, two nitrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom.
Urea molecular wt: 60.06g/mol.
The structural formula of urea is H₂N-CO-NH₂. In this structure, the carbon atom is at the center, double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O), and single-bonded to two amino groups (-NH₂).
The urea molecule has a planar geometry around the central carbon atom.
The carbon-oxygen double and carbon-nitrogen single bonds are in the same plane. The bond angles around the carbon atom are approximately 120° due to the sp² hybridization of the carbon atom’s valence electrons. The two amino groups are in a trans-configuration relative to each other, which means they are on opposite sides of the carbon-oxygen double bond
Urea does not have structural isomers because its structure is uniquely defined by the arrangement of its atoms. However, it can exist in different tautomeric forms. Tautomers are structural isomers that differ only in the position of a hydrogen atom and the location of a double bond.
In the case of Urea, the keto-enol tautomerism can occur, although the keto form (H₂N-CO-NH₂) is the most stable and predominant form under normal conditions.

Tech Blog Urea Industrial Use When most people hear the word “urea,” they immediately think of fertilizer. While it’s true that over 90% of the

Tech Blog How Is Urea Made for AdBlue AdBlue, the critical diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) for SCR systems, relies on high-purity urea (≥99.8%) as its

Tech Blog adBlue refractometer urea concentration testing AdBlue is the key to SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) systems, which rely on a precise 32.5% urea and

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE