
Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of streptococcus thermophilus
Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in


In heavy transportation, urea has become a key component in reducing harmful emissions from diesel trucks. Urea for trucks, it is commonly referred to as AdBlue or Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF), which is a carefully prepared, non-toxic, transparent, and odorless liquid solution. It comprises 32.5% high-purity urea and 67.5% deionized water and is a technology to combat nitrogen oxide (NOx) pollution.
DEF urea is not a fuel additive; It is stored in a separate fuel tank on the truck and is a component of the vehicle’s exhaust after-treatment system. DEF is a mandatory requirement for most modern diesel trucks, especially those manufactured since 2010, to comply with strict air quality regulations such as EPA standards in the United States and Euro 6 standards in Europe.
A selective catalytic reduction system is a post-combustion emission control system used for diesel trucks to reduce nitrogen oxides, which cause smoke, acid rain, and respiratory diseases. The working principle of the SCR system is to inject a water-based urea solution (AdBlue) into the exhaust stream, where it decomposes into ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). Then, ammonia reacts with nitrogen oxides under the action of a catalyst, converting these harmful gases into harmless nitrogen (N₂) and water (H₂O):
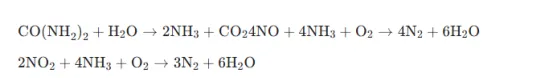
Strict emission standards: The EU’s Euro 6 standard, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) 2010 standard, and China’s National VI standard require diesel engines to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by up to 90%. The main driving force for using DEF is to meet strict international emission standards. Without it, modern trucks would be unable to comply with regulations, resulting in legal consequences.
Fuel efficiency: Unlike other emission control systems such as exhaust gas recirculation and EGR, SCR allows the engine to operate optimally by reducing fuel consumption by 3-5% as the exhaust gas is cleaned after “post-treatment” to achieve complete combustion.
Protecting public health: By neutralizing nitrogen oxide emissions, DEF helps improve air quality, reduce smoke, and
Engine lifespan: Cleaner exhaust gas means less residue accumulates in the engine and exhaust system, which may reduce maintenance costs over time.
Global adoption rate: Over 90% of new heavy-duty diesel trucks worldwide are equipped with SCR systems, driving demand for automotive urea.
Possible problems caused by impurities in urea:
Blocking SCR fuel injectors: Even trace metals such as iron and copper can cause corrosion and blockage of the fuel injection system.
Toxic catalyst: Biuret reduces catalyst efficiency, producing higher nitrogen oxide emissions.
Antifreeze protection: Deionized water can prevent mineral deposition, which may interfere with urea’s freezing point-lowering effect.
ISO 22241: International standard defining the characteristics of AdBlue, including freezing point (-11 ° C), pH value (7.5-9.5), and maximum impurity level.
Regional differences:
Europe: Compliant with ISO 22241 and EN 22241 standards.
North America: Complies with ASTM D5191 and API 1191 standards.
China: Following GB 29518-2013.
Urea consumption depends on several factors, including vehicle type, engine size, and driving conditions.
On average, a heavy-duty truck consumes 2-5% of diesel fuel in AdBlue. For example, a car that travels 100000 miles per year and has a fuel economy of 6 miles per gallon will use approximately 3300-8300 gallons of AdBlue annually.
Most modern trucks have a dedicated DEF tank that needs to be refilled regularly. Using urea will trigger a warning, reduce engine power, and even prevent the engine from starting.
DEF urea is non-toxic and safe to handle but corrosive to certain metals such as aluminum. Therefore, it should be stored in dedicated high-density polyethylene or stainless steel containers. It is recommended to store it in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place away from direct sunlight.
Common problem:
Crystalline deposits: Insufficient mixing of urea in the exhaust gas can lead to the formation of crystals, which can clog the SCR system.
Sensor malfunction: AdBlue liquid level or temperature sensor malfunction can trigger false alarms.
Preventive measures:
Regular system inspection: Clean the fuel injectors and catalysts regularly.
Quality control: Only use certified AdBlue to minimize pollution risks.
Efficient catalyst: The next generation of catalysts (such as zeolite-based catalysts) can operate at lower temperatures, improving the efficiency of urea conversion in stop-and-go traffic.
Vehicle-mounted urea production: Research on in-situ urea generation from ammonia and carbon dioxide can eliminate the need for external refueling. However, this is still in the experimental stage.
Hydrogen fuel cells: Although hydrogen trucks are emerging, diesel trucks will continue to dominate for decades, ensuring stable urea demand.
Biozones: Biozones generated from agricultural waste or biogas provide carbon-neutral alternatives, and projects in Europe and North America are exploring their feasibility.
Urea for trucks is not only a compliance tool but also a tool for optimizing the energy efficiency of heavy-duty trucks. With the tightening of emission standards and the strengthening of global efforts to combat air pollution, the role of urea in SCR systems will only become increasingly significant.

Tech Blog Study on the effect of melamine on the growth of Streptococcus thermophilus Streptococcus thermophilus is a key lactic acid bacterium widely used in

Tech Blog Melamine Modified Polyurethane Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer celebrated for its excellent wear resistance, oil resistance, chemical stability, and strong adhesion to

Tech Blog Spectrophotometric Method for Melamine Detection The spectrophotometric method for melamine detection is based on the complexation reaction between melamine powder, formaldehyde, and carbonyl
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE