
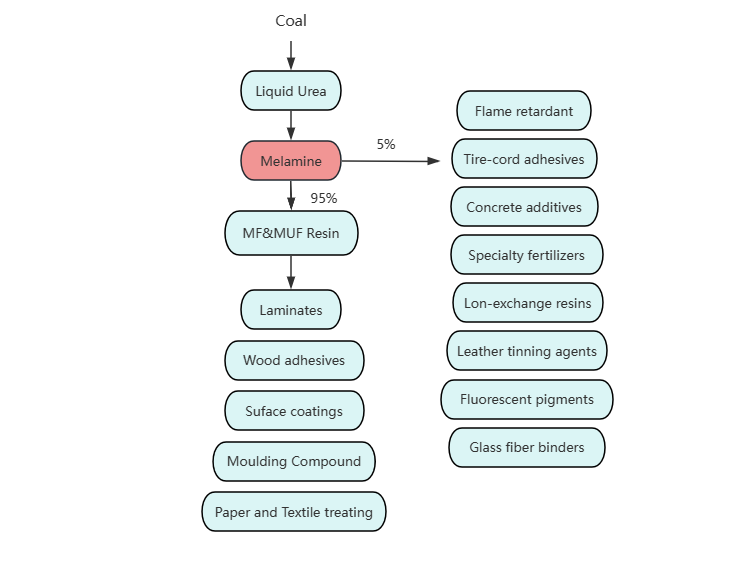
Melamine is a big market, it expands and covers a wide spectrum of growing applications. Melamine powder can be found in many things of our daily life. 95% of melamine add formaldehyde made into Mf resin. Then it can use in laminates, moulding compound, wood adhesives and so on. Others used in flame retardant, concrete additives, tire-cord adhesives, specialty fertilizers, galss fiber binders and so on.
1. Stable quality and stable production. The reaction speed is high, and big reaction volumn per unit time at high temperature in liquid phase reaction.
2. High purity. High pressure melamine powder quality is stable with less black spot due to no catalyst in reaction, however there is more black spot for Normal pressure.
3. High whiteness and high application yield. High-pressure Melamine is especially suitable for the production of high-end Amino molding powder, high-end impregnated paper, high-end flame retardant and other additives.
4. Mesh size distribution is a key feature of High pressure melamine.


High Pressure Melamine | ||
Production Tech | Tsinghua-Tech | Euro-Tech |
Purity | melamine powder 99.8% | melamine powder 99.9% |
Price | Cheaper price with high capacity | Higher price |
Apperance | Finer particle size | Coarser particle size with better flow rate |
Bulk Density | 0.50-0.55g/cm3 | 0.73g/cm3, load more in container |
Application | MDF, Impregnated paper, Tableware | Besides the above, also in high-end products such as tableware and paintings |
High Pressure Melamine is one of melamine powder divided from production tech. Representatives in the world include New Nissan process, European technology and Montedison process.
Solid urea is melted and pressurized to 9.8MPa. The residual melamine and unreacted urea in the tail gas released from the reactor, absorbing through the high-pressure scrubber, and then enter the melamine reactor. The liquid ammonia is pressurized to 10.0MPa and heated to 400 ℃ enters the reactor, and under the conditions of 10.0MPa and 380, 400℃, urea is converted into
melamine.
The washed tail gas is absorbed by the tail gas recovery device to form methylamine, which is sent out of the boundary area for further treatment. The liquid material coming out of the reactor further reacts with the hot ammonia gas in the ammonia decomposer, and the condensation polymer is decomposed into melamine, which enters the quenching tower to obtain a crude melamine slurry at 180°C and a mass fraction of 20%-30%.
Hydrogen and carbon dioxide are stripped out in the tower, and then filtered and lowered to normal pressure. Melamine crystallizes into a solid. After centrifugal separation, drying, and crushing, the finished product of melamine is obtained with a yield of 85% to 90%.
ETCE process flow: After the urea solution sent from the urea unit is concentrated, 145°C molten urea is obtained, which is pressurized to 8.5MPa and mixed with 8.5MPa and 420°C ammonia before entering the melamine reactor. The reaction pressure is 8.0MPa and the temperature At 380°C, urea is directly converted into melamine in the reactor. The liquid phase material containing carbon dioxide, ammonia, melamine and a small amount of condensation polymer coming out of the reactor is decompressed to 2.5MPa and enters the quenching section.
The ammonia and carbon dioxide are flashed out and sent out in the form of methylamine for further treatment. The melamine solution coming out of the bottom of the quenching tower is sent to the stripping tower to completely strip out the remaining ammonia and carbon dioxide, and then decomposes the condensation polymer.
After removal of solid impurities and adsorption and decolorization, crystallization, centrifugal separation, and drying are performed to obtain melamine products, with yields of 85% and 90%; the mother liquor produced by centrifugal separation undergoes ammonia recovery and wastewater treatment, and the ammonia and process water are recycled to achieve Recycling purposes.
This process technology was developed by the Italian company Monte Edison in 1962. This process uses a high-pressure liquid phase method, with a reactor temperature of 370°C and an operating pressure of 7MPa. No catalyst is used in the process. The reactor effluent is quenched with an aqueous solution of NHs and CO2, and the melamine slurry is retained in the quencher for a period of time to decompose unconverted urea and by-products.
The product needs to be treated with NaOH and activated carbon and recrystallized. The high-pressure exhaust gas can be returned to the urea production unit or the supporting small urea production unit.

JINGJIANG MELAMINE POWDER
© JINJIANG MELAMINE